What'sNEW Jul - Sep 2019
| 26 Sep 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
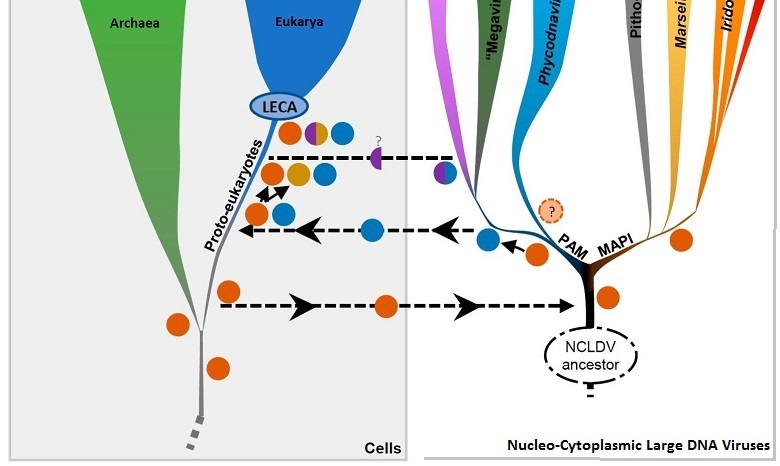 Essential eukaryotic genes are very old and are shared with large viruses.
This observation comes from a study that uses eight highly-conserved genes to draw a phylogenetic tree of large eukaryotic viruses. Among the eight were three RNA polymerases. One of them apparently predates the divergence of archaea and eukaryotes (lowest orange dot). Its variants likely crossed between the viruses and the predecessor of eukaryotes.
Essential eukaryotic genes are very old and are shared with large viruses.
This observation comes from a study that uses eight highly-conserved genes to draw a phylogenetic tree of large eukaryotic viruses. Among the eight were three RNA polymerases. One of them apparently predates the divergence of archaea and eukaryotes (lowest orange dot). Its variants likely crossed between the viruses and the predecessor of eukaryotes.
Our results strongly suggest that these transfers and the diversification of NCLDVs predated the emergence of modern eukaryotes, emphasizing the major role of viruses in the evolution of cellular domains.
 Diversification of giant and large eukaryotic dsDNA viruses predated the origin of modern eukaryotes by J. Guglielmini et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1912006116, 24 Sep 2019. Diversification of giant and large eukaryotic dsDNA viruses predated the origin of modern eukaryotes by J. Guglielmini et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1912006116, 24 Sep 2019.
 Viruses ... has related examples. Viruses ... has related examples.
 Genes Older Than Earth? is possibly related. Genes Older Than Earth? is possibly related.
| 24 Sep 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
 Giant viruses encode numerous functions previously considered exclusive to cellular life, such as transfer RNA (tRNA) synthetases, translation initiation and elongation factors, and tRNAs. Now another marine virus is seen with almost 900 predicted genes, many of which have known functions only in cellular life (yellow in pie-chart of gene categories). Some are akin to ones encoding rhodopsins that respond to light and enable us to see. But half of the virus' predicted genes are unfamiliar (black in pie-chart).
Here we see more evidence that viruses carry genes they don't need, that HGT could drive macroevolutionary progress even among eukaryotes, and that "new" genes may be not new, but simply unfamiliar.
Giant viruses encode numerous functions previously considered exclusive to cellular life, such as transfer RNA (tRNA) synthetases, translation initiation and elongation factors, and tRNAs. Now another marine virus is seen with almost 900 predicted genes, many of which have known functions only in cellular life (yellow in pie-chart of gene categories). Some are akin to ones encoding rhodopsins that respond to light and enable us to see. But half of the virus' predicted genes are unfamiliar (black in pie-chart).
Here we see more evidence that viruses carry genes they don't need, that HGT could drive macroevolutionary progress even among eukaryotes, and that "new" genes may be not new, but simply unfamiliar.
 A distinct lineage of giant viruses brings a rhodopsin photosystem to unicellular marine predators by David M. Needham, Susumu Yoshizawa, Toshiaki Hosaka et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1907517116, PNAS, online 23 Sep 2019. A distinct lineage of giant viruses brings a rhodopsin photosystem to unicellular marine predators by David M. Needham, Susumu Yoshizawa, Toshiaki Hosaka et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1907517116, PNAS, online 23 Sep 2019.
 Viruses as Modulators of Interactions in Marine Ecosystems, Kiel University, 26 Sep 2019. Viruses as Modulators of Interactions in Marine Ecosystems, Kiel University, 26 Sep 2019.
 Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms cites many related examples. Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms cites many related examples.
 Thanks, Martin Langford. Thanks, Martin Langford.
Enceladus is light and bright, with miniscule surface gravity. Its average density is only ~.6, even with an ocean. This and more comes in a review of George Dyson's book about Freeman Dyson's scheme to send a spaceship there.
 Enceladus Lights Up Saturn's Inner Moons by Paul Gilster, Centauri Dreams, 19 Sep 2019. Enceladus Lights Up Saturn's Inner Moons by Paul Gilster, Centauri Dreams, 19 Sep 2019.
 Life on Europa...? has links about Jupiter's and Saturn's moons. Life on Europa...? has links about Jupiter's and Saturn's moons.
CORRECTION: The bulk density of Enceladus is 1.61 - NASA.
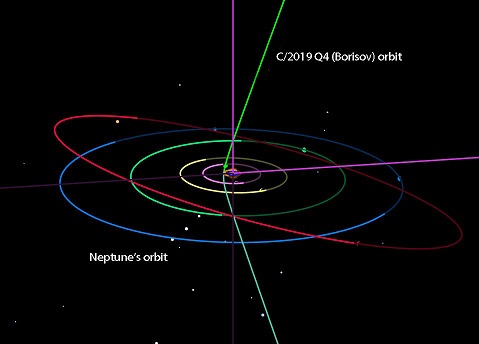 Comets can travel between stars. One with interstellar velocity should reach perihelion around December 10th. We welcome this additional, direct confirmation that comets could provide transportation for interstellar panspermia.
Comets can travel between stars. One with interstellar velocity should reach perihelion around December 10th. We welcome this additional, direct confirmation that comets could provide transportation for interstellar panspermia.
 Another Interstellar Visitor Is Headed Our Way by Bob King, Sky & Telescope, 11 Sep 2019. Another Interstellar Visitor Is Headed Our Way by Bob King, Sky & Telescope, 11 Sep 2019.
 Thanks, Centauri Dreams. Thanks, Centauri Dreams.
 Comets: The Delivery System has more. Comets: The Delivery System has more.
 Initial characterization of interstellar comet 2I/Borisov by Piotr Guzik et al., Nature Astronomy, 14 Oct 2019. Initial characterization of interstellar comet 2I/Borisov by Piotr Guzik et al., Nature Astronomy, 14 Oct 2019.
 The Man Ahead Of Time: Sir Fred Hoyle: 21-minute video tribute from IISER, Pune, posted on YouTube 09 Sep 2019. The Man Ahead Of Time: Sir Fred Hoyle: 21-minute video tribute from IISER, Pune, posted on YouTube 09 Sep 2019.
 Thanks, William Smith and Chandra Wickramasinghe. Thanks, William Smith and Chandra Wickramasinghe.
 Hoyle and Wickramasinghe's Analysis of Interstellar Dust and Hoyle and Wickramasinghe's Analysis of Interstellar Dust and
 Fred Hoyle Interviewed... have more. Fred Hoyle Interviewed... have more.
The "initial Darwinian ancestor" (IDA) was present on Earth before 4.5 billion years ago. Various kinds of life subsequently diverged, but impacts sterilized most of them to extinction before 3.85 Ga, when the earliest sediments have evidence of life. This scenario comes from a respected geophysicist who has integrated the current geological and molecular-biological data. Notably, with darwinian logic, he concludes that life is at least as old as Earth.
 Geological and Geochemical Constraints on the Origin and Evolution of Life by Norman H. Sleep, doi:10.1089/ast.2017.1778, Astrobiology, 12 Sep 2018 (the figure has been adapted); and commentary: Geological and Geochemical Constraints on the Origin and Evolution of Life by Norman H. Sleep, doi:10.1089/ast.2017.1778, Astrobiology, 12 Sep 2018 (the figure has been adapted); and commentary:
 How geology tells the story of evolutionary bottlenecks and life on Earth by Sarah Wild, NASA, 27 Oct 2018. How geology tells the story of evolutionary bottlenecks and life on Earth by Sarah Wild, NASA, 27 Oct 2018.
 Life Before 3850 Million Years Ago? has related evidence. Life Before 3850 Million Years Ago? has related evidence.
 The RNA World describes origin-of-life theories. The RNA World describes origin-of-life theories.
| 05 Sep 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
...how a genome can seemingly intentionally respond to stress and pass those favorable adaptations on to its young.
Transposable elements (TEs) are ubiquitous in eukaryotic genomes. Their activity is normally suppressed by chaperone complexes. Heat can reactivate TEs by disabling the chaperone complexes. Now, new research from Italy illuminates key details of this process. In germ cells, a specific heat shock protein, Hsp70, liberates TEs by mechanisms which differ from the ones in somatic cells. With active TEs in the germline, the next generation will have more new variants for natural selection to choose among. In this way, an experience in a parent's lifetime, heat stress, can heritably influence future generations. (This sounds like Lamarckism.) And the system is not confined to fruitflies.
The human genome is made up of perhaps 70% transposable elements. How in the world has this ongoing internal attack not driven all life to extinction? The answer is because transposable elements are kept in check by a number of mechanisms in cells, including piRNAs.... This exquisite system involves the formation of a "library" of transposable elements encoded in an organism's genome, a codex of all of the transposable elements the organism has ever encountered, a reference to which all other sequences can be compared....The piRNA system is limited to the germ plasm, where its components are loaded into eggs and sperm....
 Stress: An evolutionary mutagen by Keith A. Maggert, PNAS, 03 Sep 2019. Stress: An evolutionary mutagen by Keith A. Maggert, PNAS, 03 Sep 2019.
Cappucci, Noro et al. have probed the details of an important evolutionary mechanism, a kind of "adaptive mutation". In response to stress, the next generation is born with new variation, unlocked by programming already in the genome.
In the presence of drastic environmental changes, Hsp70 plays a key dual role in increasing both the survival probability of individuals and the genetic variability in their germ cells. The consequent increase of genetic variation in a population potentiates evolutionary plasticity and evolvability.
 The Hsp70 chaperone is a major player in stress-induced transposable element activation by Ugo Cappucci, Fabrizia Noro et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1903936116, PNAS, 03 Sep 2019. The Hsp70 chaperone is a major player in stress-induced transposable element activation by Ugo Cappucci, Fabrizia Noro et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1903936116, PNAS, 03 Sep 2019.
 Robust Software Management... is incomplete. Robust Software Management... is incomplete.
 Sub-surface oceans on nearby moons and Pluto, and the implications for life there, are surveyed by Meghan Bartels, with an entertainng 6-minute video, posted on Space.com, 03 Sep 2019. Sub-surface oceans on nearby moons and Pluto, and the implications for life there, are surveyed by Meghan Bartels, with an entertainng 6-minute video, posted on Space.com, 03 Sep 2019.
 Thanks, Ronnie McGhee. Thanks, Ronnie McGhee.
 Life on Europa, Other Moons, Other Planets? and Earth-analogs for those environments has related links. Life on Europa, Other Moons, Other Planets? and Earth-analogs for those environments has related links.
| 03 Sep 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
 ...the transcription of one [retrotransposon] can modify the higher-order 3D structure of chromatin during early primate development.
...the transcription of one [retrotransposon] can modify the higher-order 3D structure of chromatin during early primate development.
 Jumping retroviruses nudge TADs apart by Michael I. Robson and Stefan Mundlos, re: Jumping retroviruses nudge TADs apart by Michael I. Robson and Stefan Mundlos, re:
 Transcriptionally active HERV-H retrotransposons demarcate topologically associating domains in human pluripotent stem cells by Yanxiao Zhang et al., Nature Genetics, 19 Aug 2019.We observe that viruses and the elements they introduce play a powerful, essential role in macroevolutionary progress, even among eukaryotes. We think the evidence is overwhelming. Transcriptionally active HERV-H retrotransposons demarcate topologically associating domains in human pluripotent stem cells by Yanxiao Zhang et al., Nature Genetics, 19 Aug 2019.We observe that viruses and the elements they introduce play a powerful, essential role in macroevolutionary progress, even among eukaryotes. We think the evidence is overwhelming.
 Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms cites hundreds of related examples. Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms cites hundreds of related examples.
Directed mutation can produce convergent evolution. That's the conclusion we draw from a report by an international, interdisciplinary team who asked how vision in fish was quickly adapted to changed light. Only 10,000 years ago, Atlantic herring colonized the Baltic Sea, where the light is redder. Their eyes needed to adapt. The helpful adaptation came with the substitution of a single amino acid, effected by the same point mutation at the same location on the same gene, multiple times in different species. The mutation red-shifted the color-receptor and became fixed. Exactly what was needed.
We categorize adaptations like this as microevolution, and we are pleased that the specific genetic changes underlying this example are known. We suspect that software management capabilities within genomes make such directed mutation possible. Else it seems magical. We hope that understanding how genomes are able to conduct directed mutation will become an active topic for study.
...visual adaptation to the new light environment was achieved through a recent and rapid selective sweep on a mutation in the rhodopsin gene. Furthermore, this exact same amino acid change has occurred at least 20 separate times in fish species transitioning from marine to brackish or freshwater environments. This is a remarkable example of convergent evolution.
 Recurrent convergent evolution at amino acid residue 261 in fish rhodopsin by Jason Hill et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1908332116, PNAS, 26 Aug 2019. Recurrent convergent evolution at amino acid residue 261 in fish rhodopsin by Jason Hill et al., doi:10.1073/pnas.1908332116, PNAS, 26 Aug 2019.
 Convergent Evolution has related discussion. Convergent Evolution has related discussion.
 Robust Software Management... is a related, incomplete webpage. Robust Software Management... is a related, incomplete webpage.
 08 Apr 2019: ...regulated mutagenesis mechanisms greatly increase the probability that the useful mutations will occur at the right time, ...and, possibly, in the right places. 08 Apr 2019: ...regulated mutagenesis mechanisms greatly increase the probability that the useful mutations will occur at the right time, ...and, possibly, in the right places.
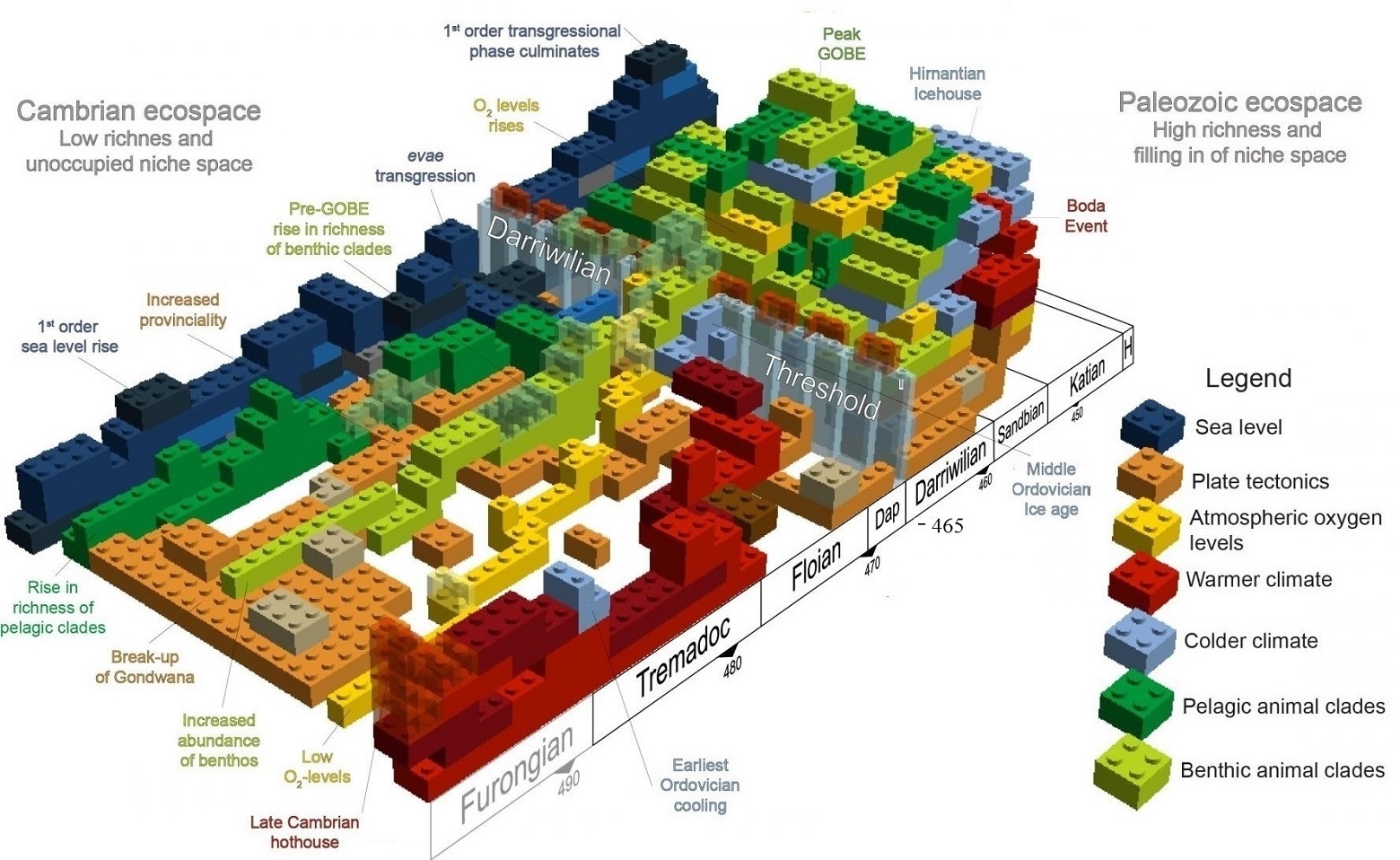
Paleologists have analyzed the Ordovician surge in biodiversity by reviewing and synthesizing the fossil and sedimentary records. They observe that simultaneous changes in temperature, atmospheric oxygen and ocean nutrients, around 465 million years ago, were necessary. They further conclude that rapid speciation was facilitated when populations were alternately connected and isolated, because sea level fluctuated as the South Polar ice cap shrank and grew. They treat these several developments as building blocks needed to climb a high barrier which they call the Darriwilian Threshold (see figure). Although the darwinian paleologists never address any apparently sudden genetic changes, we truly enjoy the postmodern landscape illustrating the changing environment as life developed.
 Coordinated biotic and abiotic change during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event: Darriwilian assembly of early Paleozoic building blocks by Alycia Stigall et al., Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 15 Sep 2019. Coordinated biotic and abiotic change during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event: Darriwilian assembly of early Paleozoic building blocks by Alycia Stigall et al., Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 15 Sep 2019.
 Early Species Developed Much Faster Than Previously Thought, Newswise, 16 Aug 2019. Early Species Developed Much Faster Than Previously Thought, Newswise, 16 Aug 2019.
 Gaia has background and updates. Gaia has background and updates.
 Neo-Darwinism... discusses fitness landscapes and punctuated equilibrium. Neo-Darwinism... discusses fitness landscapes and punctuated equilibrium.
et seq.
 Dust from asteroid breakup ...may have led to a boom in animal life by Joshua Sokol, Science, 18 Sep 2019. Dust from asteroid breakup ...may have led to a boom in animal life by Joshua Sokol, Science, 18 Sep 2019.
 Dust from a giant asteroid crash caused an ancient ice age, Field Museum, 18 Sep 2019. Dust from a giant asteroid crash caused an ancient ice age, Field Museum, 18 Sep 2019.
 Thanks, Martin Langford. Thanks, Martin Langford.
There may be more genes in the collective human microbiome than stars in the observable universe, and at least half of these genes appear to be unique to each individual.... Harvard Medical School, 14 Aug 2019.
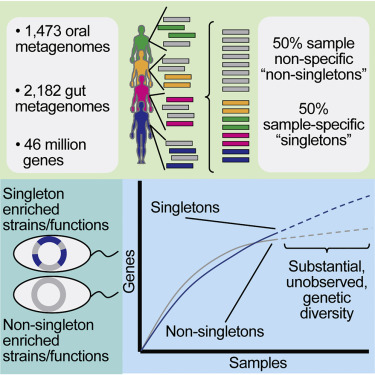
A medical team has begun the effort to sequence the entire human microbiome by starting in the digestive tract. The Boston doctors analyzed 3,500 samples containing almost 46 million genes. More than half of the genes were "singletons", unique to each individual. This ratio likely extends to the entire human microbiome, but already, the number of unfamilar genes in the digestive tract is astonishing, even to us. And the finding supports our contention that so-called "new" genes actually already exist.
 The Landscape of Genetic Content in the Gut and Oral Human Microbiome by Braden T. Tierney et al., doi:10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.008, Cell Host & Microbe, 14 Aug 2019. The Landscape of Genetic Content in the Gut and Oral Human Microbiome by Braden T. Tierney et al., doi:10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.008, Cell Host & Microbe, 14 Aug 2019.
 Microbial Fingerprinting by Ekaterina Peshiva, Harvard Medical School (+Technology Networks), 14 Aug 2019. Microbial Fingerprinting by Ekaterina Peshiva, Harvard Medical School (+Technology Networks), 14 Aug 2019.
 Thanks, Google Alerts. Thanks, Google Alerts.
 Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? and Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? and
 Genes Older Than Earth? are related. Genes Older Than Earth? are related.
Archaebacteria that contain many eukaryotic signature proteins (ESPs) have been cultured. The subject species, Lokiarchaea, were first observed in deep-sea sediments. Japanese biologists needed twelve years to culture them. Now scientists hope to ascertain the purpose of their surprising ESPs, and hope this information will help to explain the evolution of complex life.
In darwinian philosophy, genes are composed by mutation-and-selection for ongoing or incipient functions. So, plausible, non-eukaryotic functions will need to be proposed for at least some of the ESPs. (But how did the genes get the programming for their eukaryote-specific functions? Nevermind.)
In cosmic ancestry, genes precede their functions. ESPs found in prokaryotes support this expectation.
 Scientists glimpse oddball microbe that could help explain ...complex life by Jonathan Lambert, Nature, 09 Aug 2019. Scientists glimpse oddball microbe that could help explain ...complex life by Jonathan Lambert, Nature, 09 Aug 2019.
 07 May 2015: Lots more about Lokiarchaea. 07 May 2015: Lots more about Lokiarchaea.
 19 Feb 2017: ESPs in Lokiarchaea and other archaebacteria. 19 Feb 2017: ESPs in Lokiarchaea and other archaebacteria.
 Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? cites similar evidence since 1996. Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? cites similar evidence since 1996.
 Genes Older Than Earth? has more. Genes Older Than Earth? has more.

 Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote-eukaryote interface by Hiroyuki Imachi et al., Nature, 15 Jan 2020. Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote-eukaryote interface by Hiroyuki Imachi et al., Nature, 15 Jan 2020.
 Meet the relatives of our cellular ancestor by Christa Schleper and Filipa L. Sousa, Nature, 15 Jan 2020. Meet the relatives of our cellular ancestor by Christa Schleper and Filipa L. Sousa, Nature, 15 Jan 2020.
 ...insight into early complex life on Earth, The Guardian, 15 Jan 2020. ...insight into early complex life on Earth, The Guardian, 15 Jan 2020.
 Thanks, Gordon Cooper. Thanks, Gordon Cooper.
A star that is "older than the universe" is baffling scientists, suggesting there might be something fundamentally wrong with the Big Bang theory.
 ...by Sophie Curtis, Daily Mirror (+ Sean Martin, Express), 08 Aug 2019. ...by Sophie Curtis, Daily Mirror (+ Sean Martin, Express), 08 Aug 2019.
 The End and the Big Bang has related discussion and updates. The End and the Big Bang has related discussion and updates.
 Thanks, Karen Roberts. Thanks, Karen Roberts.
 Darwin's Doubt, by Stephen C. Meyer, has two central theses. The first is that the modern theory of evolution does not work. In 500 pages, he makes a thorough and convincing case.
Darwin's Doubt, by Stephen C. Meyer, has two central theses. The first is that the modern theory of evolution does not work. In 500 pages, he makes a thorough and convincing case.
The second thesis is that Intelligent Design (ID) does work. Well, if so, how does it work? When Meyer mentions causes now in operation (p 349), and titles a section A Cause Now in Operation (p 360), we become especially alert. But no causes ever appear. Meyer explains that ID is not a strictly material process or mechanism (p 395). He thinks it can still be scientific.
The book would edify almost anyone interested in evolution. And the gridlock imposed by Darwinism and ID remains in place. There must be another way.
 Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent Design, by Stephen C. Meyer, Harper One, 2013. Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent Design, by Stephen C. Meyer, Harper One, 2013.
 Evolution versus Creationism has discussion and links. Evolution versus Creationism has discussion and links.
 Compare Darwinism, Creationism/ID, Cosmic Ancestry Compare Darwinism, Creationism/ID, Cosmic Ancestry
...we know that nature has been busy cross-contaminating worlds for the past 4 billion years.
 Tardigrades Were Already on the Moon by Caleb A. Scharf, Scientific American, 08 Aug 2019. Tardigrades Were Already on the Moon by Caleb A. Scharf, Scientific American, 08 Aug 2019.
 Thanks, William Smith and Stan Franklin. I thought Scharf was skeptical. Anyway, good to hear. Thanks, William Smith and Stan Franklin. I thought Scharf was skeptical. Anyway, good to hear.
 ...'Water bears' stuck on the moon after crash, BBC News, 07 Aug 2019. ...'Water bears' stuck on the moon after crash, BBC News, 07 Aug 2019.
 11 Mar 2002: Tardigrades in space? and 11 Mar 2002: Tardigrades in space? and
 18 May 2011: Project BIOKIS... are related. 18 May 2011: Project BIOKIS... are related.
...the last common ancestor of all multicellular animals ...already possessed an extremely complex genome.
 Symphony of genes, University of Vienna (+Newswise), 05 Aug 2019; re: Symphony of genes, University of Vienna (+Newswise), 05 Aug 2019; re:
 Ancient animal genome architecture reflects cell type identities by Bob Zimmermann et al., Nature Ecology & Evolution, 05 Aug 2019. Ancient animal genome architecture reflects cell type identities by Bob Zimmermann et al., Nature Ecology & Evolution, 05 Aug 2019.
 Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? cites similar evidence since 1996. Metazoan Genes Older Than Metazoa? cites similar evidence since 1996.
 Genes Older Than Earth? has more. Genes Older Than Earth? has more.
 The Enceladus data are consistent with a soup replete with highly diverse organic compounds, which could serve as chemical supply for the formation of early lifelike entities. — Three astrochemists are promoting research to identify the complex organics in Enceladus' ocean, which they believe to be a prebiotic soup. They hope that the precise mix of them could help to distinguish among several origin-of-life scenarios, namely Proteins First, Metabolism First, RNA First, and their favorite, Lipids First.
The Enceladus data are consistent with a soup replete with highly diverse organic compounds, which could serve as chemical supply for the formation of early lifelike entities. — Three astrochemists are promoting research to identify the complex organics in Enceladus' ocean, which they believe to be a prebiotic soup. They hope that the precise mix of them could help to distinguish among several origin-of-life scenarios, namely Proteins First, Metabolism First, RNA First, and their favorite, Lipids First.
 Enceladus: First Observed Primordial Soup Could Arbitrate Origin-of-Life Debate by Amit Kahana, Philippe Schmitt-Kopplin and Doron Lancet, doi:10.1089/ast.2019.2029, Astrobiology, online 22 Jul 2019.
The authors curtly dismiss the possibility that the organics might already include amino acids or other byproducts of life. They are aware that many carbonaceous meteorites contain amino acids, but apparently, not that these consistently exhibit remnant lifelike chirality. Panspermia is never mentioned. And of course, in an article about prebiotic soup, the software problem is left to others. Enceladus: First Observed Primordial Soup Could Arbitrate Origin-of-Life Debate by Amit Kahana, Philippe Schmitt-Kopplin and Doron Lancet, doi:10.1089/ast.2019.2029, Astrobiology, online 22 Jul 2019.
The authors curtly dismiss the possibility that the organics might already include amino acids or other byproducts of life. They are aware that many carbonaceous meteorites contain amino acids, but apparently, not that these consistently exhibit remnant lifelike chirality. Panspermia is never mentioned. And of course, in an article about prebiotic soup, the software problem is left to others.
 Life on Europa, Other Moons, Other Planets? has links about candidates for hosting life, including Enceladus. Life on Europa, Other Moons, Other Planets? has links about candidates for hosting life, including Enceladus.
 The RNA World and Other Origin-of-Life Theories has history and updated links. The RNA World and Other Origin-of-Life Theories has history and updated links.
 The Second Law of Thermodynamics and the six "Next" pages are all about the software problem. The Second Law of Thermodynamics and the six "Next" pages are all about the software problem.
 02 Aug 2019: George Nickas replies with comments and questions. 02 Aug 2019: George Nickas replies with comments and questions.
 ...which genes may have played a role in the evolution of the placenta of certain freshwater fish is the goal of a study by biologists mostly from Wageningen University in the Netherlands. They chose to study Heterandria formosa (pictured), because there are non-placental species in the same family, so the trail should be relatively fresh. They sequenced its genome and compared it to published genomes of three related species, to be able to identify orthologous genes among them. Ultimately they found evidence exclusively in H. formosa of five duplications, and positive selection in 18 of the orthologs. Eight of the latter are known to have placental functions in mammals. The study was sharply focussed and illuminating.
...which genes may have played a role in the evolution of the placenta of certain freshwater fish is the goal of a study by biologists mostly from Wageningen University in the Netherlands. They chose to study Heterandria formosa (pictured), because there are non-placental species in the same family, so the trail should be relatively fresh. They sequenced its genome and compared it to published genomes of three related species, to be able to identify orthologous genes among them. Ultimately they found evidence exclusively in H. formosa of five duplications, and positive selection in 18 of the orthologs. Eight of the latter are known to have placental functions in mammals. The study was sharply focussed and illuminating.
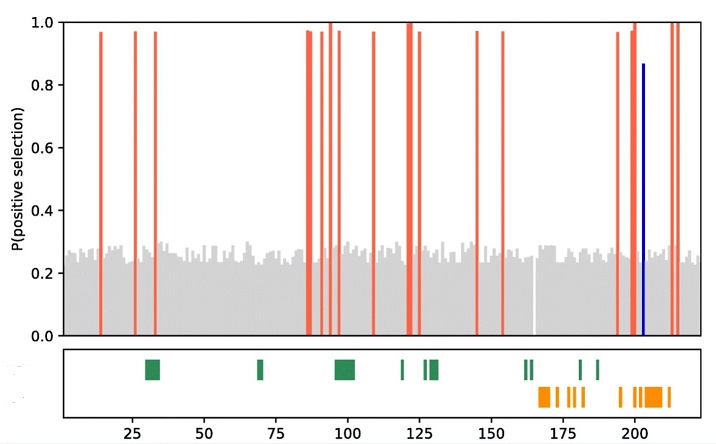
In one featured protein, 20 out of 224 residues showed strong evidence of positive selection (tall red or blue lines.) Only a few of these 20 were in the enzymatic binding sites (colored bars in lower box.) Most residues showed evidence of only neutral mutations without any detectable effect (grey-colored "lawn"). To us the changes in this protein look like optimization by directed mutation, an example of microevolution. Yet this and similar changes seem to be involved in the evolution of placental birth — macroevolution by any definition. What can be said?
First, the study was focussed on only orthologous genes. If an H. formosa gene had no orthologs in the sister species, it was ignored. We wish the Dutch team would now ask if any acquired or newly activated DNA of any description "may have played a role in the evolution of the placenta." We think that would also be illuminating.
 The genome of the live-bearing fish Heterandria formosa implicates a role of conserved vertebrate genes in the evolution of placental fish by Henri van Kruistum et al., BMC Evolutionary Biology, 26 Jul 2019. The genome of the live-bearing fish Heterandria formosa implicates a role of conserved vertebrate genes in the evolution of placental fish by Henri van Kruistum et al., BMC Evolutionary Biology, 26 Jul 2019.
 Neo-Darwinism... Neo-Darwinism...  Macroevolutionary Progress Redefined... and Macroevolutionary Progress Redefined... and
 Testing Darwinism... are related webpages. Testing Darwinism... are related webpages.
 27-30 Jul 2019: First author van Kruistum replies to our reqest for clarification. Very helpful! 27-30 Jul 2019: First author van Kruistum replies to our reqest for clarification. Very helpful!
| 23 Jul 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
...the most dramatic case known of functional horizontal gene transfer ever found in complex organisms.... includes stealing more than 100 functional genes, allowing the invasive vine to latch onto and steal nutrients from the host and even to send genetic weapons back into the host. HGT is both ancestral and an ongoing process in Cuscuta.
|
| The HGT states of each ancestral node of the species tree were inferred with two methods. Colored bars representing each method contain numbers of HGT gain-and-loss events for each ancestral and terminal node. |
 Convergent horizontal gene transfer and cross-talk of mobile nucleic acids in parasitic plants by Zhenzhen Yang et al., Nature Plants, 22 Jul 2019.
These lines of evidence all point to ...transfer of intact genomic DNA, including introns. Convergent horizontal gene transfer and cross-talk of mobile nucleic acids in parasitic plants by Zhenzhen Yang et al., Nature Plants, 22 Jul 2019.
These lines of evidence all point to ...transfer of intact genomic DNA, including introns.
 Parasitic plants steal genes to become better parasites by Nick Carne, Cosmos, 23 Jul 2019. Parasitic plants steal genes to become better parasites by Nick Carne, Cosmos, 23 Jul 2019.
 Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms has lots about the role of HGT in evolution. Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms has lots about the role of HGT in evolution.
 Thanks, Stan Franklin and Google Alerts. Thanks, Stan Franklin and Google Alerts.
 26 Aug 1996: Arlo 'n' Janis features life on Mars. 26 Aug 1996: Arlo 'n' Janis features life on Mars.
 Thanks, Polly Cooper. We shoulda posted this long ago. Thanks, Polly Cooper. We shoulda posted this long ago.
Pluto observations reveal complex organics on a small body ...in the outermost regions of the Solar System.
 Prebiotic Chemistry of Pluto by D.P. Cruikshank et al., Astrobiology, online 16 Jul 2019. Prebiotic Chemistry of Pluto by D.P. Cruikshank et al., Astrobiology, online 16 Jul 2019.
(How do they know that the organics are prebiotic?)
| 21 Jul 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
More than half of our genome consists of transposons, DNA sequences that are reminiscent of ancient, extinct viruses — from research asking what happens when DNA methylation is lost in human cells. Of interest to us, specific silent transposons may be activated, move, and affect genes that are important in the development of nerve cells.
 ...the darker parts of our genetic heritage, Lund University (+Science Daily), 19 Jul 2019. ...the darker parts of our genetic heritage, Lund University (+Science Daily), 19 Jul 2019.
 Thanks, Martin Langford. Thanks, Martin Langford.
If all of the virus genes were laid end-to-end, they would stretch 250 million light-years.
 Evolution and ecology of plant viruses by Lefeuvre, P., Martin, D.P., Elena, S.F. et al., doi:10.1038/s41579-019-0232-3, Nat Rev Microbiol, 16 Jul 2019. Evolution and ecology of plant viruses by Lefeuvre, P., Martin, D.P., Elena, S.F. et al., doi:10.1038/s41579-019-0232-3, Nat Rev Microbiol, 16 Jul 2019.
 Plant viruses may be reshaping our world, ASU via PhysOrg.com, 17 Jul 2019. Plant viruses may be reshaping our world, ASU via PhysOrg.com, 17 Jul 2019.
 Thanks, Google Alerts. Thanks, Google Alerts.
| 18 Jul 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
 Red Algae Steal Genes from Bacteria to Cope with Environmental Stresses, Rutgers Today (+Newswise), 16 Jul 2019. Red Algae Steal Genes from Bacteria to Cope with Environmental Stresses, Rutgers Today (+Newswise), 16 Jul 2019.
 The genomes of polyextremophilic cyanidiales contain 1% horizontally transferred genes with diverse adaptive functions by Alessandro W Rossoni et al., doi:10.7554/eLife.45017, eLife, 31 May 2019. The genomes of polyextremophilic cyanidiales contain 1% horizontally transferred genes with diverse adaptive functions by Alessandro W Rossoni et al., doi:10.7554/eLife.45017, eLife, 31 May 2019.
|
Making an argument for the importance of HGT in eukaryote (specifically, Cyanidiales) evolution, as we do here, requires that three major issues are addressed: a mechanism for foreign gene uptake and integration, the apparent absence of eukaryotic pan-genomes, and the lack of evidence for cumulative effects (Martin, 2017). The latter two arguments are dealt with below but the first concern no longer exists. (Could the numberless ORFan genes, in viruses for example, make up much of the eukaryotic pan-genome? And we see plenty of cumultive effects.) |
 Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms has lots about the role of HGT in evolution. Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms has lots about the role of HGT in evolution.
Hayabusa2 touched down on Ryugu to collect material from beneath the surface.
 Japanese spacecraft probes asteroid's guts for first time, Nature News, 10 Jul 2019. Japanese spacecraft probes asteroid's guts for first time, Nature News, 10 Jul 2019.
Gary Ruvkun, a principal investigator in the Search for Extraterrestrial Genomes (SETG), openly advocates panspermia in a recent interview. We welcome his message, with two minor reservations. First, he is obligated to concede that methane "can be produced by various chemical reactions." As Fred Hoyle once commented, if methane could be readily made chemically, Germany would have won World War II. Second, Ruvkun cannot safely oppose standard big-bang dogma. Still, for the origin-of-life, he comments that he would rather have "a hundred billion years of time or a thousand billion years of time. That would be more satisfying." To efficiently look for life beyond Earth, he wants to send DNA sequencing equipment to Mars. Great idea!
 What If Life Did Not Originate on Earth? by Isaac Chotiner, The New Yorker, 08 Jul 2019. What If Life Did Not Originate on Earth? by Isaac Chotiner, The New Yorker, 08 Jul 2019.
 Thanks, Glenda Ruby. Thanks, Glenda Ruby.
 06 Jan 2017: more on Ruvkun. 06 Jan 2017: more on Ruvkun.
The linked interview led us to his recent TED-style lecture explaining how genomics and early life point to panspermia:
 Gary Ruvkun: Breakthrough Discuss 2019, YouTube, 17 Apr 2019. Gary Ruvkun: Breakthrough Discuss 2019, YouTube, 17 Apr 2019.
On the same podium Robert Zubrin talks about DNA as a way to transmit coded information through space. He suggests that propaganda might motivate extraterrestrials to advertise to other worlds. We weren't convinced, but he soon mentions propagation, which life does automatically, naturally. Plenty to learn from Zubrin.
 ...Interstellar Communication with Microbes..., YouTube, 17 Apr 2019. ...Interstellar Communication with Microbes..., YouTube, 17 Apr 2019.
 21 Dec 2017: more on Zubrin. 21 Dec 2017: more on Zubrin.
 How is it Possible? includes our early speculations about intentionally undertaking panspermia to avoid extinction. How is it Possible? includes our early speculations about intentionally undertaking panspermia to avoid extinction.
| 10 Jul 2019 | What'sNEW about HGT  | | |
 ...a large insertion of DNA from the endosymbiont bacteria Wolbachia ...integrated itself directly into the pillbug chromosome, essentially creating an entirely new sex chromosome via horizontal gene transfer.
...a large insertion of DNA from the endosymbiont bacteria Wolbachia ...integrated itself directly into the pillbug chromosome, essentially creating an entirely new sex chromosome via horizontal gene transfer.
Before a bacterial gene can even operate in a eukaryotic cell, it has some major biological hurdles to overcome. It must acquire introns, a promoter sequence, and a termination sequence. It also has to be able to interact fruitfully with existing host genes. ...Researchers are trying to understand how this enormous leap occurs.
...against slim odds, some of these bacterial genes have introduced novel and critical functions to their new hosts. These transfers, say researchers, are an overlooked source of fodder for evolutionary transformation in complex organisms.
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is not overlooked in cosmic ancestry. We think it is essential for evolutionary progress. We highly recommend the new open-access review article by Viviane Callier.
 ...Gene transfers from bacteria and viruses may be shaping complex organisms, doi:10.1073/pnas.1909030116, by Viviane Callier, PNAS, 09 Jul 2019. ...Gene transfers from bacteria and viruses may be shaping complex organisms, doi:10.1073/pnas.1909030116, by Viviane Callier, PNAS, 09 Jul 2019.
 Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms is our main related webpage. Viruses and Other Gene Transfer Mechanisms is our main related webpage.
 Robust Software Management in Genomes begins our attempt "to understand how this enormous leap occurs." Robust Software Management in Genomes begins our attempt "to understand how this enormous leap occurs."
Astronomers and cosmologists are beginning to promote the likelihood of interstellar panspermia. Yesterday Harvard publicised a calculation by members of its astronomy department showing that asteroids may be accelerated from the galactic center fast enough to carry life throughout the Milky Way galaxy.
 Study suggests asteroids might play key role in spreading life by Peter Reuell, posted on Physorg.com (originally Harvard Gazette), 09 Jul 2019. Study suggests asteroids might play key role in spreading life by Peter Reuell, posted on Physorg.com (originally Harvard Gazette), 09 Jul 2019.
 Thanks, Ted Steele. Thanks, Ted Steele.
 11-15 Oct and 11-15 Oct and
 09 Feb 2018: more about this study.
Recently ( 09 Feb 2018: more about this study.
Recently ( 23 Jun) another astronomer reported that neighboring stars may swap life-bearing cometary material frequently. We welcome endorsements of panspermia, but these recent studies are only about the transfer of physical material. It would be fanciful to assert that life is out there without the pioneering work by Fred Hoyle (1915-2001) and Chandra Wickramasinghe (b. 1939). Beginning in the 1960s, they made careful spectrographic analyses of interstellar dust. By 1980 they had found solid evidence for organic molecules and even whole bacteria in the dust. Their research gave interstellar panspermia its most substantial support. 23 Jun) another astronomer reported that neighboring stars may swap life-bearing cometary material frequently. We welcome endorsements of panspermia, but these recent studies are only about the transfer of physical material. It would be fanciful to assert that life is out there without the pioneering work by Fred Hoyle (1915-2001) and Chandra Wickramasinghe (b. 1939). Beginning in the 1960s, they made careful spectrographic analyses of interstellar dust. By 1980 they had found solid evidence for organic molecules and even whole bacteria in the dust. Their research gave interstellar panspermia its most substantial support.
 Hoyle and Wickramasinghe's Analysis of Interstellar Dust has an historical outline. Hoyle and Wickramasinghe's Analysis of Interstellar Dust has an historical outline.
 Comets: The Delivery System has more. Comets: The Delivery System has more.
 04 July 2019: Chandra Wickramasinghe reviews the development of cometary panspermia theory. 04 July 2019: Chandra Wickramasinghe reviews the development of cometary panspermia theory.
![]()
|
 Essential eukaryotic genes are very old and are shared with large viruses.
This observation comes from a study that uses eight highly-conserved genes to draw a phylogenetic tree of large eukaryotic viruses. Among the eight were three RNA polymerases. One of them apparently predates the divergence of archaea and eukaryotes (lowest orange dot). Its variants likely crossed between the viruses and the predecessor of eukaryotes.
Essential eukaryotic genes are very old and are shared with large viruses.
This observation comes from a study that uses eight highly-conserved genes to draw a phylogenetic tree of large eukaryotic viruses. Among the eight were three RNA polymerases. One of them apparently predates the divergence of archaea and eukaryotes (lowest orange dot). Its variants likely crossed between the viruses and the predecessor of eukaryotes.
 Giant viruses encode numerous functions previously considered exclusive to cellular life, such as transfer RNA (tRNA) synthetases, translation initiation and elongation factors, and tRNAs. Now another marine virus is seen with almost 900 predicted genes, many of which have known functions only in cellular life (yellow in pie-chart of gene categories). Some are akin to ones encoding rhodopsins that respond to light and enable us to see. But half of the virus' predicted genes are unfamiliar (black in pie-chart).
Here we see more evidence that viruses carry genes they don't need, that HGT could drive macroevolutionary progress even among eukaryotes, and that "new" genes may be not new, but simply unfamiliar.
Giant viruses encode numerous functions previously considered exclusive to cellular life, such as transfer RNA (tRNA) synthetases, translation initiation and elongation factors, and tRNAs. Now another marine virus is seen with almost 900 predicted genes, many of which have known functions only in cellular life (yellow in pie-chart of gene categories). Some are akin to ones encoding rhodopsins that respond to light and enable us to see. But half of the virus' predicted genes are unfamiliar (black in pie-chart).
Here we see more evidence that viruses carry genes they don't need, that HGT could drive macroevolutionary progress even among eukaryotes, and that "new" genes may be not new, but simply unfamiliar. Comets can travel between stars. One with interstellar velocity should reach perihelion around December 10th. We welcome this additional, direct confirmation that comets could provide transportation for interstellar panspermia.
Comets can travel between stars. One with interstellar velocity should reach perihelion around December 10th. We welcome this additional, direct confirmation that comets could provide transportation for interstellar panspermia.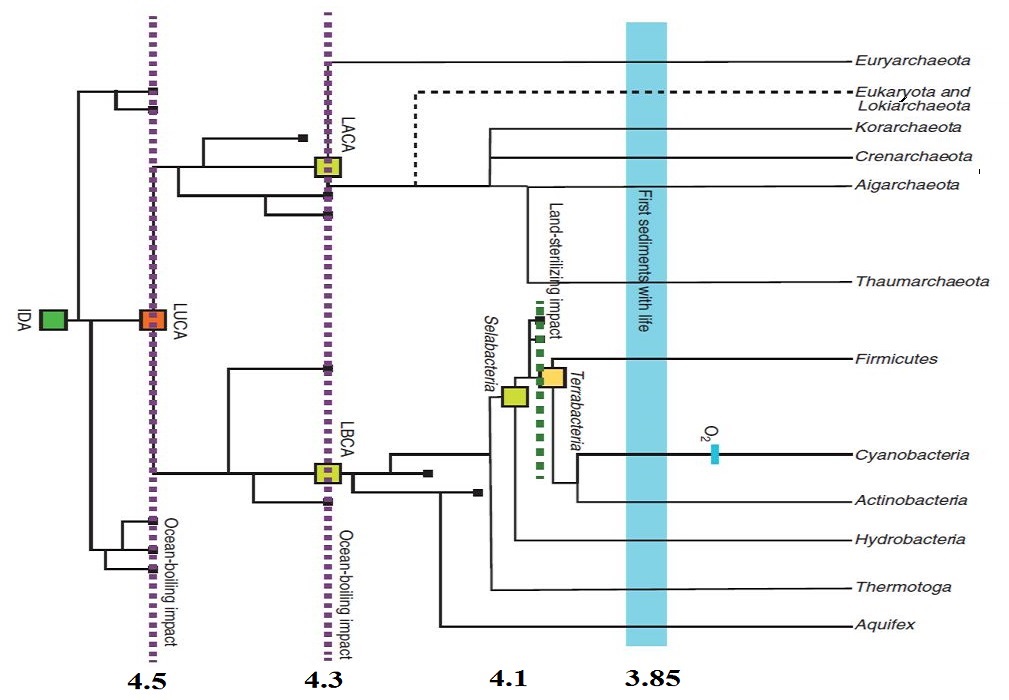
 ...the transcription of one [retrotransposon] can modify the higher-order 3D structure of chromatin during early primate development.
...the transcription of one [retrotransposon] can modify the higher-order 3D structure of chromatin during early primate development.

 Darwin's Doubt, by Stephen C. Meyer, has two central theses. The first is that the modern theory of evolution does not work. In 500 pages, he makes a thorough and convincing case.
Darwin's Doubt, by Stephen C. Meyer, has two central theses. The first is that the modern theory of evolution does not work. In 500 pages, he makes a thorough and convincing case.
 The Enceladus data are consistent with a soup replete with highly diverse organic compounds, which could serve as chemical supply for the formation of early lifelike entities. — Three astrochemists are promoting research to identify the complex organics in Enceladus' ocean, which they believe to be a prebiotic soup. They hope that the precise mix of them could help to distinguish among several origin-of-life scenarios, namely Proteins First, Metabolism First, RNA First, and their favorite, Lipids First.
The Enceladus data are consistent with a soup replete with highly diverse organic compounds, which could serve as chemical supply for the formation of early lifelike entities. — Three astrochemists are promoting research to identify the complex organics in Enceladus' ocean, which they believe to be a prebiotic soup. They hope that the precise mix of them could help to distinguish among several origin-of-life scenarios, namely Proteins First, Metabolism First, RNA First, and their favorite, Lipids First. ...which genes may have played a role in the evolution of the placenta of certain freshwater fish is the goal of a study by biologists mostly from Wageningen University in the Netherlands. They chose to study Heterandria formosa (pictured), because there are non-placental species in the same family, so the trail should be relatively fresh. They sequenced its genome and compared it to published genomes of three related species, to be able to identify orthologous genes among them. Ultimately they found evidence exclusively in H. formosa of five duplications, and positive selection in 18 of the orthologs. Eight of the latter are known to have placental functions in mammals. The study was sharply focussed and illuminating.
...which genes may have played a role in the evolution of the placenta of certain freshwater fish is the goal of a study by biologists mostly from Wageningen University in the Netherlands. They chose to study Heterandria formosa (pictured), because there are non-placental species in the same family, so the trail should be relatively fresh. They sequenced its genome and compared it to published genomes of three related species, to be able to identify orthologous genes among them. Ultimately they found evidence exclusively in H. formosa of five duplications, and positive selection in 18 of the orthologs. Eight of the latter are known to have placental functions in mammals. The study was sharply focussed and illuminating.
 ...a large insertion of DNA from the endosymbiont bacteria Wolbachia ...integrated itself directly into the pillbug chromosome, essentially creating an entirely new sex chromosome via horizontal gene transfer.
...a large insertion of DNA from the endosymbiont bacteria Wolbachia ...integrated itself directly into the pillbug chromosome, essentially creating an entirely new sex chromosome via horizontal gene transfer.
